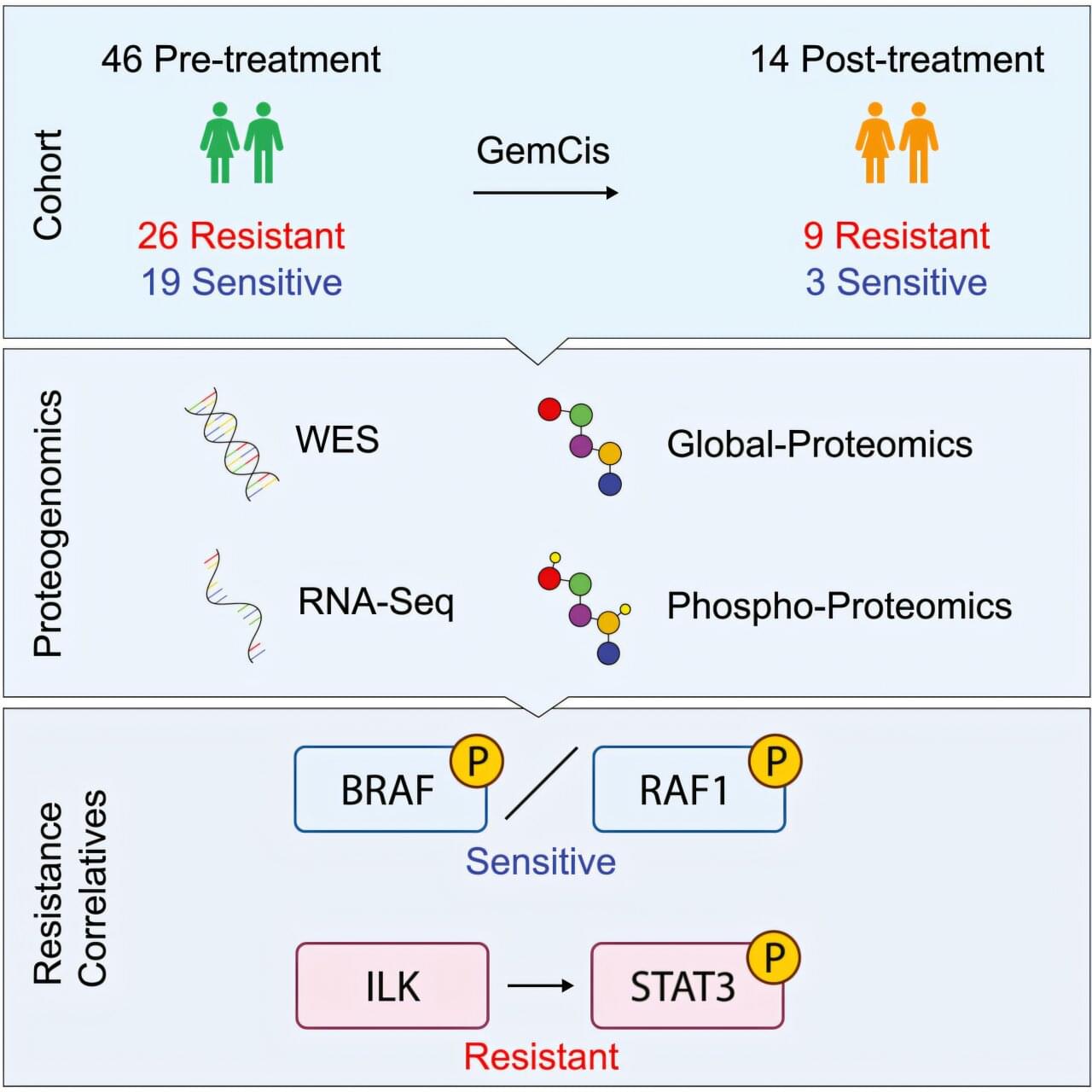
About one quarter of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) may be treated and derive a benefit with the current standard chemotherapy. To better understand why some tumors resist chemotherapy and identify better ways to treat those cancers, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have conducted a detailed molecular analysis of MIBC tumors. The results, published in Cell Reports Medicine, offer potential new ways to identify which patients will benefit from chemotherapy and reveal possible new treatment strategies.
“One of our goals was to identify molecular markers in patient tumors that would help us predict which patients were most likely to benefit from chemotherapy and which ones might not,” said first co-author, Dr. Matthew V. Holt, director of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center Proteomics Laboratory at Baylor.
The researchers studied 60 MIBC tumor samples using a comprehensive multi-omics approach which included genomics (sequencing the genes of the tumor), transcriptomics (analyzing which genes are turned on or off), proteomics (the proteins produced by the tumor) and phosphoproteins (proteins with chemical tags that control their activity).